
Yupik art represents a vibrant tapestry of cultural expression, deeply intertwined with the history, environment, and spiritual beliefs of the Yupik people of Alaska and Siberia. For generations, these indigenous communities have crafted intricate masks, carvings, textiles, and other art forms that reflect their unique worldview. However, the preservation of this rich artistic heritage faces numerous challenges, including climate change, cultural assimilation, and the loss of traditional knowledge. This article delves into the various Yupik art preservation efforts underway, highlighting the strategies, challenges, and the importance of community involvement.
What is Yupik Art?
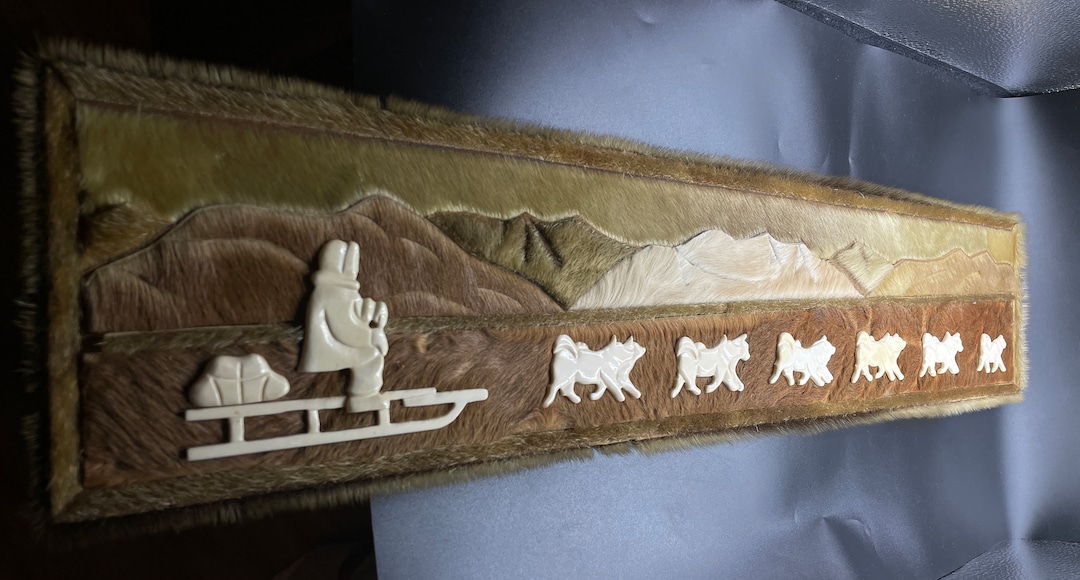
- Masks: Elaborate masks used in ceremonies, often depicting spirits or animals.
- Carvings: Intricate carvings made from ivory, wood, and bone, representing animals, people, and mythical figures.
- Textiles: Baskets, clothing, and other items woven from natural materials like grass and animal fibers.
- Storytelling: Oral traditions and performances that transmit history, values, and beliefs.
These art forms are not static; they evolve over time, reflecting changes in Yupik society and the environment. However, the core principles and cultural significance remain constant, making preservation efforts all the more critical.
Why is Yupik Art Preservation Important?
- Cultural Identity: Art is a cornerstone of Yupik cultural identity, connecting people to their heritage and traditions.
- Historical Record: Art provides valuable insights into the history, beliefs, and way of life of the Yupik people.
- Traditional Knowledge: Art often incorporates traditional knowledge about the environment, animals, and sustainable practices.
- Community Empowerment: Preservation efforts can empower Yupik communities by fostering pride in their heritage and providing economic opportunities.

The loss of Yupik art would be a devastating blow to the Yupik people and to the world’s cultural heritage. Therefore, ongoing preservation efforts are essential to ensure that these traditions continue to thrive.
Challenges to Yupik Art Preservation
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and melting permafrost are damaging archaeological sites and traditional materials used in art.
- Cultural Assimilation: The influence of Western culture can lead to the abandonment of traditional practices and languages.
- Loss of Traditional Knowledge: As elders pass away, their knowledge of traditional art techniques and cultural meanings may be lost.
- Lack of Resources: Many Yupik communities lack the financial resources and infrastructure needed to support preservation efforts.
- Accessibility: Many artifacts are housed in museums far from the Yupik communities.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that involves collaboration between Yupik communities, museums, researchers, and funding organizations.
Key Yupik Art Preservation Efforts
Community-Based Initiatives
- Language Revitalization: Programs to teach and promote the Yupik language, which is essential for understanding the cultural context of art.
- Traditional Arts Education: Workshops and classes where elders teach younger generations traditional art techniques.
- Cultural Centers: Community centers that showcase Yupik art, host cultural events, and provide a space for intergenerational learning.
- Oral History Projects: Recording and preserving the stories and knowledge of elders.
These community-based initiatives are crucial because they empower Yupik people to take ownership of their cultural heritage and ensure its transmission to future generations.
Museum Partnerships
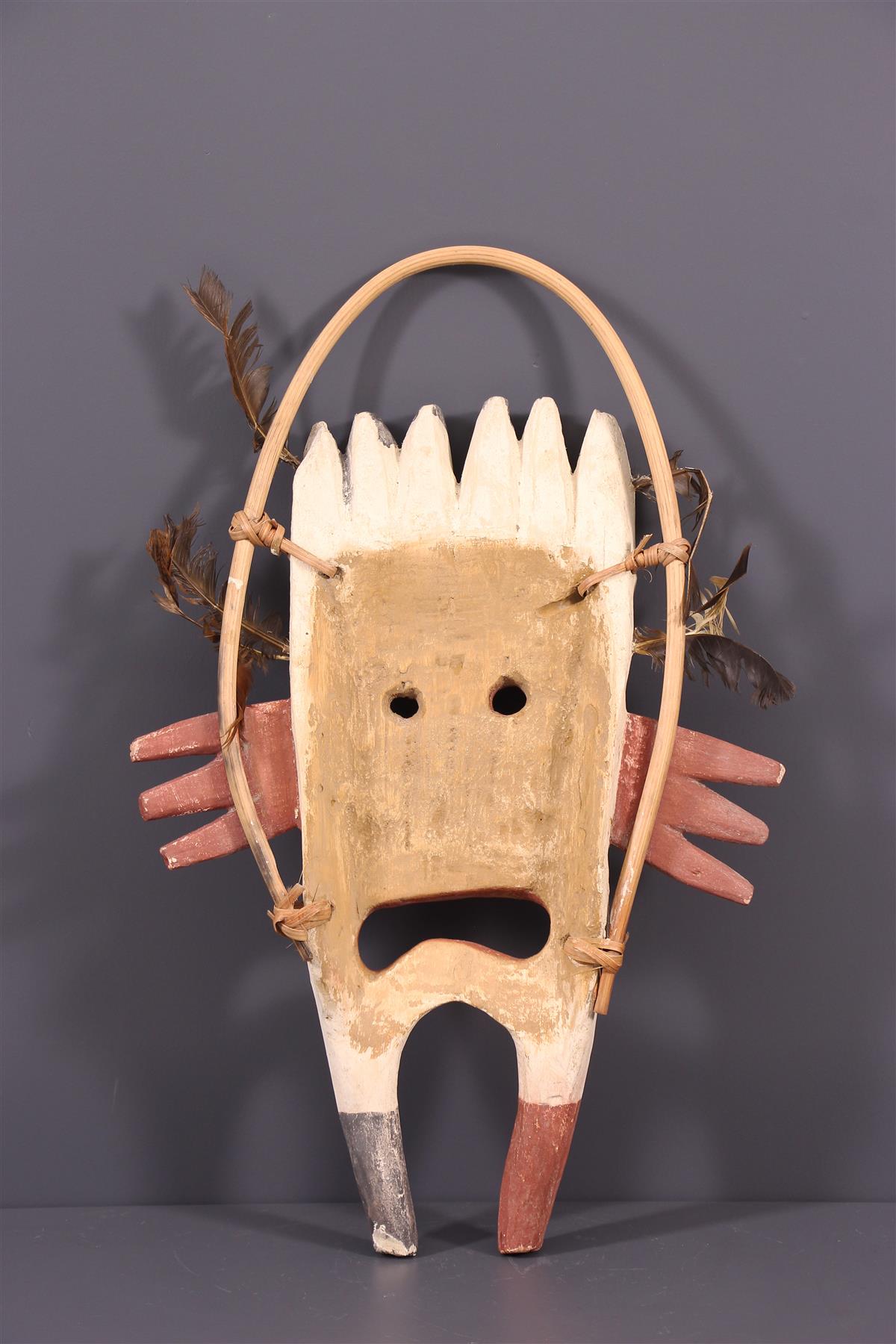
- Collection Management: Proper storage and conservation of Yupik artifacts to prevent deterioration.
- Exhibitions: Creating exhibitions that educate the public about Yupik art and culture.
- Research: Conducting research on Yupik art to deepen understanding of its history and significance.
- Community Engagement: Collaborating with Yupik communities to ensure that exhibitions and research are culturally sensitive and relevant.
- Digital Archives: Creating digital archives that make Yupik art accessible to a wider audience.
Successful museum partnerships prioritize collaboration with Yupik communities, ensuring that their voices and perspectives are central to the preservation and interpretation of their art.
Digital Preservation
- Digitization of Artifacts: Creating high-resolution digital images and 3D models of Yupik art objects.
- Online Archives: Developing online archives that make Yupik art accessible to researchers, educators, and the general public.
- Virtual Reality: Creating virtual reality experiences that allow people to explore Yupik art and culture in an immersive way.
- Interactive Storytelling: Using digital media to create interactive stories that teach about Yupik art and its cultural context.
Digital preservation efforts can help to overcome geographical barriers and make Yupik art accessible to a global audience. However, it is essential to ensure that these efforts are culturally sensitive and respect the intellectual property rights of Yupik communities.
Funding and Support
- Government Grants: Grants from federal, state, and local government agencies.
- Private Foundations: Funding from philanthropic organizations that support cultural preservation.
- Corporate Sponsorships: Financial support from businesses that are committed to cultural heritage.
- Individual Donations: Contributions from individuals who are passionate about Yupik art and culture.
Securing adequate funding is essential for sustaining long-term preservation efforts and ensuring that Yupik communities have the resources they need to protect their cultural heritage.
The Role of Education
- School Programs: Integrating Yupik art and culture into school curricula.
- University Courses: Offering courses on Yupik art, history, and culture at universities and colleges.
- Public Lectures: Organizing lectures and workshops for the general public to raise awareness about Yupik art.
- Online Resources: Creating online educational resources that are accessible to students, teachers, and the general public.
By educating people about Yupik art and culture, we can foster a greater appreciation for its value and importance, and inspire future generations to become stewards of this rich heritage.
Addressing Common Questions (People Also Ask)
What are some examples of traditional Yupik art?
Traditional Yupik art includes masks used in ceremonies, intricate carvings from ivory and wood, woven baskets and textiles, and storytelling performances. These art forms often depict animals, spirits, and scenes from daily life, reflecting the Yupik worldview and connection to the environment.
How is climate change affecting Yupik art?
Climate change poses a significant threat to Yupik art. Rising temperatures and melting permafrost are damaging archaeological sites, causing the deterioration of organic materials used in art (such as ivory and wood), and disrupting traditional hunting and gathering practices that provide materials for art.
What can I do to support Yupik art preservation efforts?
You can support Yupik art preservation efforts by donating to organizations that support Yupik communities and cultural preservation, visiting museums and cultural centers that showcase Yupik art, purchasing art directly from Yupik artists, and educating yourself and others about Yupik culture.
How are Yupik communities involved in preserving their art?
Yupik communities are actively involved in preserving their art through language revitalization programs, traditional arts education, cultural centers, oral history projects, and collaborations with museums and researchers. These initiatives empower Yupik people to take ownership of their cultural heritage and ensure its transmission to future generations.
Where can I see Yupik art?
You can see Yupik art in museums and cultural centers in Alaska, such as the Anchorage Museum, the University of Alaska Museum of the North, and the Yupik Science Center. Many online resources and virtual exhibits also showcase Yupik art, making it accessible to a global audience.
The Future of Yupik Art Preservation
- Strengthening Community-Based Initiatives: Supporting Yupik communities in their efforts to revitalize their language, teach traditional arts, and preserve their cultural knowledge.
- Expanding Museum Partnerships: Fostering collaborative relationships between museums and Yupik communities to ensure that exhibitions and research are culturally sensitive and relevant.
- Leveraging Digital Technologies: Utilizing digital technologies to create online archives, virtual exhibits, and educational resources that make Yupik art accessible to a global audience.
- Securing Sustainable Funding: Identifying and securing long-term funding sources to support preservation efforts.
- Raising Public Awareness: Educating the public about the value and importance of Yupik art and culture.
Conclusion
Yupik art is a testament to the resilience, creativity, and cultural richness of the Yupik people. Preserving this art is not only a matter of safeguarding historical artifacts but also of honoring the living traditions and cultural identity of the Yupik communities. Through collaborative efforts, innovative strategies, and a deep commitment to community empowerment, we can ensure that Yupik art continues to inspire and enrich the world for generations to come. The preservation efforts are a vital investment in cultural heritage, community well-being, and the future of Yupik culture.
By supporting Yupik art preservation, you directly contribute to the vitality and continuation of a unique and significant cultural legacy. It’s a way to honor the past, engage with the present, and invest in the future of the Yupik people and their invaluable contributions to the world’s cultural landscape.


